
|
A restrained socket or spigot joint for jacking pipes is a pipe joint which is created by inserting the plug-in end (spigot end) through the sealing ring into the socket of the next pipe or by connecting the plug-in ends (spigot ends) with a coupling. Both variants prevent the joints from being pulled apart [HDD-1]. These spigot joints are usually created in a flexible way, i.e. angularly deflectable when being used for HDD. PVCU pipes, for which … |

|
A welded joint is a rigid, restrained pipe joint, whose sealing effect is achieved by gluing together the pipe ends to be joined [HDD-1]. In the case of HDD applications, welding techniques are used for steel, PE and PVC-U pipes (see (Steel pipes), (PE-pipes) as well as (PVC-U-pipes)). Besides the joints, concerning gas and water supply, plastic pipes can also have rigid screwed and mechanical clamp joints that are mentioned in Volume 1, Sections 13.11.1.2 … |

|
According to EN 14457 [HDD-294], a pipe joint, or also simply called joint, is defined as the “connection between the adjacent ends of two components including the means of sealing and pressure transfer ring, (during installation) if applicable.” The pipe joint must ensure that the following criteria are met: -
tightness against internal and external pressure
-
transferral of longitudinal forces (here: pullback forces) whilst ensuring lateral stability,
|

|
(Image: Possible mechanical strain of the pipe coating while pulling-in)Even today, there are neither national nor European standards that define general requirements of jacking pipes irrespective of the type of pipe. A first attempt at this is the EN 12889 [HDD-9] that, in an extremely restricted form in Section 5.2 “Pipes and joints” for drains and sewers, is formulated as follows: “Installation shall not commence before the following criteria have … |

|
Steels are the most frequently used metallic materials for manufacturing pipes. According to the classic definition, steel is an alloy that consists of iron and carbon and that contains less than 2.06% (mass) carbon. EN 10020 [HDD-301] also follows this definition, according to which steels are materials whose mass proportion of iron is greater than that of any other element, whose carbon concentration is generally smaller than 2 weight per cent.… |

|
(Image: Possible mechanical strain of the pipe coating while pulling-in)Unprotected directly-buried steel pipelines can suffer external corrosion due to aggressive soils or filling materials and internal corrosions by aggressive water, low flow velocities and bacterial influences. According to DIN 50929 [HDD-407] and/or DIN 30675 [HDD-408], the probability of corrosion in soils and waters can be estimated (see (External protection)). Adequate protection … |

|
For product pipes, the external protection (coating and/or jacket) is factory-manufactured in accordance with the client’s requirements. As coatings, that are resistant to soils of all aggressiveness classes (see (External protection)) according to DIN 50929 [HDD-407] the following plastic coatings can be considered: -
PE coating according to DIN 30670 [HDD-323]
-
PP coating according to DIN 30678 [HDD-324]
(Image: Layer structure of gas and water pipelines … |

|
(Image: Recoating a pipe joint of a PE-coated water pipeline by means of a plastic tape that is workable in a cold state (one-tape system) according to DIN 30672 and/or DIN EN 12068)Before pulling-in the pipelines, all site-manufactured pipe joints, such as the pipe barrel or shaft, must be protected against corrosion by so-called recoating or field coating and, if required, mechanically by socalled re-jacketing [HDD-15] [HDD-359] [HDD-330]. This … |

|
Organic coating systems that are workable in a cold state (cold systems) such as petrolatum/soft paraffin tapes and plastic tapes are not warmed during application. This is why these systems need to be sufficiently ductile under ambient temperature, so they can be applied to the surface of the steel pipe without developing cavities. Furthermore, the area to be coated needs to be slightly heated during preparatory cleaning by using a gas flame; this … |

|
Thermoprocessable recoating systems are workable in a warm state (warm systems) and are applied onto the pipe area to be coated by external energy input (mostly with a liquid gas or propane gas torch). The classic representative of this group is the bitumen tape. The supply of heat serves the purpose of melting the bitumen. In a plastic condition, it is then glued onto the pipe surface, possibly on a previously applied, adhesion promoting precoating (… |

|
In the following, several external protection systems that have proven themselves for use in the pulling-in process in HDD are introduced as examples. They are used as a recoating of organic coating systems (inner ply) or as independent external protection. They can be classified as follows: -
duroplastic plastic external protection based on polyurethane,
-
duroplastic plastic jacketing based on epoxy resin,
-
jacketing with cement bandages or cast mortar,
|

|
(Image: Recoating a pipe joint of a PE-coated water pipeline by means of a plastic tape that is workable in a cold state (one-tape system) according to DIN 30672 and/or DIN EN 12068)Before pulling-in the pipelines, all site-manufactured pipe joints, such as the pipe barrel or shaft, must be protected against corrosion by so-called recoating or field coating and, if required, mechanically by socalled re-jacketing [HDD-15] [HDD-359] [HDD-330]. This … |

|
(Image: Possible mechanical strain of the pipe coating while pulling-in)Unprotected directly-buried steel pipelines can suffer external corrosion due to aggressive soils or filling materials and internal corrosions by aggressive water, low flow velocities and bacterial influences. According to DIN 50929 [HDD-407] and/or DIN 30675 [HDD-408], the probability of corrosion in soils and waters can be estimated (see (External protection)). Adequate protection … |

|
Linings serve for applying a compact layer onto the inner pipe wall as a protection against physical, biological, chemical and/or biochemical attacks from the inside and to prevent the development of incrustations [HDD-43]. In the case of application at hand it is exclusively referred to coatings. This is a collective term for one or several continuous layers that are manufactured of coating substances [HDD-355]. |
|
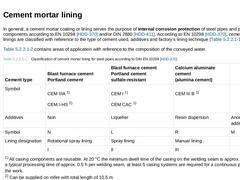
In general, a cement mortar coating or lining serves the purpose of internal corrosion protection of steel pipes and pipeline components according to EN 10298 [HDD-370] and/or DIN 2880 [HDD-411]. According to EN 10298 [HDD-370], cement mortar linings are classified with reference to the type of cement used, additives and factory’s lining technique (Table 61). Table 62 contains areas of application with reference to the composition of the conveyed … |

|
To reduce friction in high-pressure pipelines over very long distances and thus to increase the flow and to reduce energy consumption, epoxy- or PU-based lining according to ISO 15741 [HDD-356], EN 10301 [HDD-357], for example, and/or API RP 5L2 [HDD-358] in gas pipes, for instance, can be applied (so-called Flow-Coat) [HDD-328]. This very thin lining, which has been used now for offshore pipelines for gas transport for a long time, does not prevent … |

|
Linings serve for applying a compact layer onto the inner pipe wall as a protection against physical, biological, chemical and/or biochemical attacks from the inside and to prevent the development of incrustations [HDD-43]. In the case of application at hand it is exclusively referred to coatings. This is a collective term for one or several continuous layers that are manufactured of coating substances [HDD-355]. |

|
Considering the pressure levels that can be achieved, the operating conditions and the fluid transported, the pipe material steel offers a wide range of connection techniques, especially butt-welded joints or welded sockets or spigot joints [HDD-359]. Due to their absolute axial restraint, in practice only steel pipelines with butt welded joints are used for pulling-in by means of HDD. Alternatively, for water pipelines, especially in the case of … |

|
(Image: Design of a heated tool or butt fusion welded joint (vertical down weld) [349])Due to the high economic efficiency and the special suitability for construction sites, usually for gas and water pipelines, the arc welding with stick electrode according to EN 499 [HDD-361] is used (cf. also DVGW GW 350 [HDD-362]). In pipeline construction, in this regard, stick electrodes that are wrapped with cellulose and are welded together vertically, have … |

|
The welding seams created at the construction site must be tested for defects and cracks in a non-destructive manner. Besides the test seams, for the construction site area only non-destructive tests come into question and in particular (Table 66) [HDD-330]: -
visual inspection,
-
liquid penetration test,
-
ultrasonic inspection,
-
radiographic inspection.
Type and extent of the non-destructive testing need to be arranged with experts especially for high-… |

|
Lacking free space for the mounting of the pipeline strings either requires the time-consuming welding of single pipes inside the starting pit or the use of restrained plug and socket joints, which is common in water supply. Depending on the pullback force applied on steel pipes of the diameter range of DN/ID 80 to DN/ID 300, two designs of a friction plug-in socket of the type TYTON®- SIT (see (Joints of ductile cast iron pipes)) and DKM (Table … |

|
Considering the pressure levels that can be achieved, the operating conditions and the fluid transported, the pipe material steel offers a wide range of connection techniques, especially butt-welded joints or welded sockets or spigot joints [HDD-359]. Due to their absolute axial restraint, in practice only steel pipelines with butt welded joints are used for pulling-in by means of HDD. Alternatively, for water pipelines, especially in the case of … |

|
(Image: Figure 214 Preferable external diameter and wall thicknesses for steel pipes according to DIN EN 10208-1 (marked by the framed field including frame))The construction length of steel pipes usually ranges between 6 m and 18 m [HDD-360]. Depending on the wall thickness and the type of pipe joint, for gas and water pipes, the maximum operating pressures that are required and given in the corresponding manufacturing standards can be applied. … |

|
Steels are the most frequently used metallic materials for manufacturing pipes. According to the classic definition, steel is an alloy that consists of iron and carbon and that contains less than 2.06% (mass) carbon. EN 10020 [HDD-301] also follows this definition, according to which steels are materials whose mass proportion of iron is greater than that of any other element, whose carbon concentration is generally smaller than 2 weight per cent.… |

|
Ductile cast iron is a ductile iron-carbon material whose carbon content predominantly consists of graphite in free form. Ductile cast iron mainly differs from the grey cast iron, which is nowadays no longer used for buried supply and discharge lines, in the shape of graphite particles [HDD-379]. Grey cast iron contains lamellar graphite, whereas ductile cast iron contains graphite spheres or spheroidal graphite. The shape of graphite mainly influences … |