
|
A cleaning plan should be based on a demand and condition oriented cleaning strategy, where only sections showing deposits and debris are cleaned. During cleaning, their structural condition is taken into account. This allows for the reduction of the costs incurred during cleaning and the avoidance of excessive stress on the pipes. A demand- and condition-oriented cleaning plan has the objectives to: -
Reduce the number of reactive cleaning measures …
|

|
The starting point for the development of demand- and condition-oriented cleaning plans is a description of the drain and sewer system, the analysis of previous cleaning methods (devices, equipment, staff, selected operational parameters, logistics, documentation of disturbances/incidents/failures, complaints, trouble spots, accessibility difficulties, etc.) and previous cleaning expenses (strategy and costs, etc.) in order to identify the economic … |

|
"Planning is the conceptual anticipation of steps that seem necessary to achieve an objective. In the process, it is taken into consideration by which means the objective is to be achieved, how these means are to be applied and how the achieved results are to be controlled." [ [Wiki2001]] The achievement of the objective must not be taken for granted, because, to a large extent, the plan is always based on assumptions. It illustrates the complex interrelations … |

|
Inspection plans are developed based on the "review and description of the drain and sewer system" that has been realised in step 1. Their purpose is to determine the on-site situation regarding the formation of deposits and the need for planned cleaning measures. Inspection plans combine statements with respect to the deposition behaviour from various operational processes, as for example in the course of manhole or shaft inspections (accessed by … |

|
Following the acquisition of deposit data from the individual sections and manholes, the findings are classified and assessed. An example of a three-step model for the classification and assessment of data, which has been developed and applied in several research projects [ [Orth2008]] [ [Bosse2004]] [ [Freit2005]] is shown in Table 3‑4. Depending on both the size and structure of the drain and sewer system, other, more advanced assessment criteria, … |

|
Based on the technical assessment and prioritisation of the deposit situation in the drain and sewer system and as part of the strategic cleaning plan, the resulting data is combined with the objectives mentioned in (Cleaning objectives and strategies). The final results show a prioritisation and area ranking (Image 3‑6). In addition to a technical assessment of the deposits, the results also include environment-related, operational, hydraulic, economic … |

|
The cleaning measures are carried out based on operative cleaning planning in the form of operational or flushing plans. These plans include a priority ranking of the determined cleaning measures, specifying both the cleaning method of choice and associated cleaning devices and tools ( (Cleaning of drains and sewers)). Furthermore, the method-specific performance parameters are determined and specified considering the structural condition of the … |

|
|

|
In step 3, the cleaning planning is implemented based on the developed operational and flushing plans. During cleaning, the collected waste is to be checked as regularly as possible. A higher proportion of mineral solids and broken pipe bits indicates serious damage, e.g. pipe fracture or collapse. In such situations, the cleaning procedures have to be stopped immediately and protective measures have to be taken. If required, a less destructive cleaning … |

|
After the cleaning measures are completed, a quality control is carried out in step 4. Subsequently, the cleaning services and results are documented. This ensures that inadequately or insufficiently performed cleaning measures can immediately be detected, and the service provider can be asked to undertake improvements. Furthermore, quality control inclusive of appropriate documentation (Table 3‑2) ensures a constant update of the much needed operational … |

|
|

|
(Image: Overview of the drain and sewer cleaning methods as per [Führb1980]) There exist numerous methods for the cleaning of drainage systems (Image 3‑14). They are applied based on the cleaning objective and the structure specific, local, structural and hydraulic limiting conditions. Selection of cleaning measures must be in accordance with EN 14654-1 [ [EN14654-1:2005]], and should also take into account the technical feasibility and economic viability … |

|
High-pressure cleaning is the use of high-pressure equipment to remove obstacles and deposits in drains and sewers [ [EN14654-1:2005]]. This universal method, which is applied in about 90% of all sewer cleaning measures in Europe, is also used as a preparatory action prior to an inspection (section 4.1.2 - in progress) or a rehabilitation (2nd volume of Rehabilitation and Maintenance of Drains and Sewers - in progress) [ [Geib2002]]. The process of … |
|
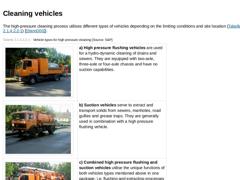
The high-pressure cleaning process utilises different types of vehicles depending on the limiting conditions and site location (Image 3‑17) [ [SteinD00]]. (Table: Vehicle types for high pressure cleaning) The flushing water required for cleaning is taken from the water supply network via stand pipes and sand filters. A direct connection to a hydrant is prohibited. Generally, a permission under the Water Act and a specially equipped high-pressure flushing … |
|
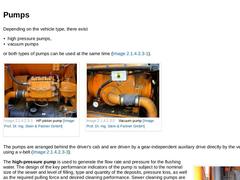
Depending on the vehicle type, there exist -
high pressure pumps,
-
vacuum pumps
or both types of pumps can be used at the same time (Image 3‑20). (Image: HP piston pump) (Image: Vacuum pump) The pumps are arranged behind the driver's cab and are driven by a gear-independent auxiliary drive directly by the vehicle's motor using a v-belt (Image 3‑21). (Image: Pumps drive system) The high-pressure pump is used to generate the flow rate and pressure for the … |

|
Hoses The hoses used for high pressure cleaning are divided into High pressure flushing hoses (Image: Arrangement of the large and small hose reel on the combined high pressure flushing and suction vehicle with water recovery technology ) High pressure flushing hoses, subsequently also called HP-flushing hoses or hose, serve to transport the flushing water under high pressure to the nozzle, and have to … |

|
Suction tubes (Image 3‑26) are used to extract the waste material collected in the manhole. (Image: Extraction of the waste material from a manhole using a suction tube) In practice, abrasion-proof rubber tubes are used for this purpose. They have to meet the following requirements [ [Geib2002]]: -
Resistance to internal and external abrasion
-
Ability to withstand the maximum negative pressure generated by the vacuum pump
-
Low internal frictional resistance
|

|
|

|
The nozzle is described in [ [Brock1952]] as the mouthpiece of the pipe which is used to narrow the flow channel, thus transforming pressure into velocity (pressure nozzle) or velocity into pressure (suction nozzle). Nozzles used for cleaning purposes (subsequently also called cleaning nozzles) serve to generate the required jets of liquid (pressurised water jets, in literature often called high-pressure water jets) to -
Propel the flushing hose from …
|

|
Fluid jets, which also include pressurised water jets, are free jets by definition, because they form a fluid flow that passes through a nozzle that is then emitted into the open air without restrictions [ [Kraat1989]] [ [Rinal2003]] [ [Freim1998]]. The following case involves circular non-restricted turbulent free jets (water jets) in the medium of air. They are characterised by exchanges that are triggered by the turbulent diffusion at the edges … |

|
Cleaning nozzles are designed depending on the type and quantity of sedimentations and deposits, or rather the type of obstacle, the cross sectional shape of the sewer, and the cleaning objective (Table 3‑13). They are categorised into: -
Radial nozzles (pressurised water jets emerge radially backwards, distributed along the length/extent of the nozzle)
-
Rotary nozzles (like radial nozzle, in addition, the cleaning nozzle rotates)
-
Penetrator nozzles (…
|

|
In recent years, special forms of cleaning nozzles have been developed in addition to the above-mentioned standard nozzle types in the attempt to expand the range of high-pressure cleaning application. One such special nozzle is referred to as the invert cleaner or seeing nozzle as it allows for both cleaning and inspection (Image 3‑36) [ [SteinR04]]. This so-called invert cleaner is used to remove deposits in drains and sewers with the assistance … |

|
|

|
For an effective use of high-pressure cleaning, a precise knowledge of the occurring pressure losses is very important. A distinction is drawn between: -
Pressure loss at the vehicle,
-
Pressure loss in the high-pressure flushing hose and
-
Pressure loss in the nozzle.
According to [ [Orth2008]], depending on the cleaning nozzle and the nozzle inserts, as well as the characteristics of the high-pressure flushing hose (material, nominal size, length), … |

|
The highest pressure losses can be found in the high pressure flushing hose. According to [ [Geib2002]], the calculation of these losses, resulting from the turbulent flow, is performed using Equation 3‑7. (Formula: Pressure loss in the high-pressure flushing hose) According to this equation, the pressure loss in the high-pressure flushing hose is inversely proportional to the internal diameter and the hose length, the squared mean flow velocity and … |