
|
Transducer and measuring instruments Various transducers or measuring instruments are necessary in order to acquire the measuring information required by the methods of measurement described above. According to DIN 19559-1 [ [DIN19559-1:1983]], these should be “robust and low-maintenance” and measure “without any extra impairment of the flow cross section with a high degree of flow constancy, uninfluenced by extreme environment-related conditions, … |

|
Flow velocity measurement Flow velocity measurement may relate to the velocity of a flow. Direct measurement of mean flow velocity – Magnetic inductive velocity sensors and through flow measurement devices (MID) MID-transducers rely on the electrical conductivity of the sewage. The basis of this measurement principle is Faraday´s law of induction: a voltage is induced in a conductor that is positioned at right angle to the lines … |

|
For the measurement of local velocities the application of: -
mechanical measuring propellers and
-
MID velocity sensors
has predominantly proven itself.
Mechanical flow measuring propellers
Mechanical flow measuring propellers (Image 4‑204) (Image 4‑205) are precision instruments with friction resistant bearing mounted propeller blades whose speeds of revolution are directly proportional to the flow velocity in the pipe to be measured. From the propeller’…
|
|
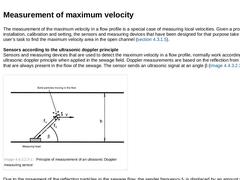
The measurement of the maximum velocity in a flow profile is a special case of measuring local velocities. Given a proper installation, calibration and setting, the sensors and measuring devices that have been designed for that purpose take over the user’s task to find the maximum velocity area in the open channel ( (Measuring procedure)).
Sensors according to the ultrasonic doppler principle
Sensors and measuring devices that are used to detect the … |

|
|

|
It is becoming increasingly common to measure the volumetric flow by means of instruments with flow depth and velocity sensors combined in a single detector housing (Image 4‑208). This trend mirrors the user’s desire for measurement systems that are both compact and easy to handle in their installation and that do not require any fixtures for a cross sectional reduction. The measurement and evaluation methods of these instruments are always based … |

|
|

|
|

|
Operational inspection measures serve to investigate the causes and effects of operating problems under normal operating conditions in a drain and sewer system. They may also be needed to investigate failures in the system. Together with the structural investigation measures, they are called "inspection" [ [DWAM149-5:2010]]. Operating problems occur when operational functional requirements (section 1.11) cannot be met within a drain and sewer system, … |

|
Investigation is the first of the four fundamental activities included in integral sewer management. To a reasonable extent, it is to cover all performance aspects of the drain and sewer system in order to create the basis for the next step (the evaluation of the capacity of the drain and sewer system). The obtained results serve to show compliance to due diligence, and also as the basis for the determination of all activities to be carried out with respect to rehabilitation and maintenance. That is why volume 4 of "Rehabilitation and Maintenance of Drains and Sewers" deals with the investigation and inspection. |

|
(Image: 85004 - Titelbild Dokumentation) Process: Lining with GRP discrete pipes Title: Renovation of a brickwork ovoid cross section DN 600/900 by lining with GRP discrete pipes Location: Inner city area Limiting conditions: - System: Combined wastewater sewer
- Material: Brickwork
- Cross section: Ovoid
- Nominal size: DN 1600/2000, DN 1200/2000
- Depth position: 4.0 - 4.5 m
- Groundwater: not present
- Gradient: 5.9 - 23.3 ‰
- Length of section: 8 sections per approximately …
|

|
Maschinen und Geräteeinsatz - 1 HGV
- 1 Excavator
- Trench lining elements
- 1 High-pressure flushing vehicle
- 1 Inspection vehicle
- 1 Electric crane
- 1 Capstan winch
- 1 Pipe transportation vehicle
- 1 Silo vehicle
- 1 Mixing and pump mobile
- Sealing balloons circular cross section DN 100 - 250
- 1 Compressor
- 1 Drilling machine with various adaptors
- 1 Angle grinder operated with compressed air
Tools - Trowel
- Folding rule
- Paint roller
- Hammer
- Rubber hammer
(Image: GRP pipes, … |

|
Site equipment Site equipment includes traffic safety, provision and preparation of storage surfaces for equipment and material as well as the provision of power and water supplies. In this particular case the water supply is ensured by nearby hydrants. Water retention To maintain the drainage capability, the clear cross section of the sewers is shut with brickwork, but with an inlet above the certain section that to be rehabilitated. A relief of the … |

|
Driving-in excavations Due to the selected pipe lengths of 1.0 m or 3.0 m and the selected way of installation "driving-in method" it is impossible to install the pipes via the extant manholes. Thus, in the case at hand the GRP pipes are installed via supported driving-in excavations, which are arranged near the sections, with an approximate dimension of 2.0 m x 4.0 m. In the driving-in excavations the old brickwork profile is exposed and is broken … |

|
Preparatory measures At the target shaft a 5-ton capstan winch is prepared for the pulling-together of the GRP pipes. (Image: Capstan winch at the target shaft) Installation of the GRP pipes The GRP pipes stored near the driving-in excavation are let down into the excavation by means of an electric crane or HGV and are positioned in the section that is exposed to the springing line. | (Image: Storing of the GRP pipes) | (Image: Letting down the GRP pipes … |
|

|
Due to the non-straight course of the old sewer's path and the restrictions for the installation resulting from it as well as the hydraulic over-dimensioning of the old sewer the nominal size of the GRP pipes that are to be installed was determined with DN 470/705 in the rehabilitation planning. The thus caused relatively large annular space of up to approximately 15.0 cm in the crown area and the shape of the cross section "ovoid" (entrance angle … |

|
After the GRP pipes are installed and laterals are recovered the continuous pipes are connected by a GRP fitted piece inside the driving-in excavation. The joints between the fitted piece and the continuous pipe are sealed with hand laminate. Before filling the driving-in excavation, a PVC line is installed on the crown of the GRP pipes over the entire length of the excavation in order to enable the flow of filling material from section to section … |

|
Preparatory measures Before grouting of the annular space, each at the beginning and at the end of the each section the annular space has to be shut in such professional way that the grouting pressure can be taken up and a control of the grouting procedure is enabled. In the case at hand the annular space was grouted with concrete and each a filling nozzle DN 100 and a ventilation nozzle DN 50 were installed. An approximately 2.0 m long PVC-pipe is … |

|
Manhole rehabilitation During the optical inspection predominantly the following damages were noticed: - missing joint material,
- missing or defective clinkers,
- defective manhole installations,
- unprofessionally built laterals.
| (Image: Corroded manhole installations) |
(Image: Corroded joints inside the manhole channel) |
(Image: Corroded joints inside the manhole channel) |
The extant manhole bases are rehabilitated by lining with GRP channels and -plates … |

|
After the grouting of the annular space is completed, the leaktightness of the installed continuous pipe of GRP pipes is to be proved by a leaktightness testing according to EN 1610. The testing pressure is 100 mbar and has to be maintained during the testing time of 8 min. If the measured pressure loss at the end of the testing is smaller than the permitted value of 15 mbar, the test requirements are met. The leaktightness testing is to be documented … |

|
Renovation of a brick sewer with a DN 600/900 egg-shaped cross-section using lining with discrete GRP pipes, in which individual pipes are joined together during installation to form a continuous pipe string. |

|
(Image: 55125 - Titelbild Dokumentation) Proess: Re-jointing corroded masonry joints, crack injection, repair of damaged laterals Title: Repair of masonry sewage collectors and manholes while retaining the original masonry by rehabilitation of the joints and crack injections. Location: Position in the road cross section of a German main road Limiting values: - System: Combined wastewater sewer, wastewater sewer
- Material: Masonry
- Cross sectional shapes: …
|

|
NOTE: The procedures described below apply equally to both collectors even if only one is mentioned. Bore core removal and soil exploration A special challenge in the planning of this rehabilitation measure was the intention of retaining the original masonry. To achieve this, comprehensive calculations of the structural bearing capacity of the old sewer were necessary. In order to obtain the entry data for the structural evaluation, a comprehensive … |

|
The rehabilitation of the masonry collectors is achieved by injection of the existing cracks and re-jointing the corroded masonry joints. With this method the corrosion protection of the collectors and their partly insufficient stability as shown by the calculations is again established. In order to determine the quality standards in the execution of the masonry rehabilitation as regards materials and procedures, three reference fields were carried … |

|
Machines and equipment - 1 Power generator
- 1 Compressor
- 1 Pressure vessel
- 1 Piston pump
Tools and equipment - Compressed air-driven angle grinder
- Boring machine
- Hammer
- Chisel
- Hand cartridge filler for joint filling
- Ribbed impact packer
- Masonry injection packer
- Quick-acting snap closure
- Trowel
- Bucket
Materials The following is a summary of the most important materials used with this method: Cement mortar (for new jointing of the previously scraped out joints): |