
|
|
|
The two methods of the spiral wound lining are used in gravity sewer with a circular profile, independent of the material of the old pipe. (Image: Construction materials used in sewers [Stein01c]) |

|
-
The spiral wound lining method without annular space filling is used in the nominal diameter range from DN 200 (200 mm or 8 inches) to DN 1200 (1200 mm or 48 inches).
-
The spiral wound lining method with annular space filling is used in the nominal diameter range from DN 500 (500 mm or 20 inches) to DN 3000 (3000 mm or 120 inches).
When using the spiral wound lining, the cross-sectional dimensions of the sewer section to be rehabilitated are reduced. … |

|
The rehabilitation length is specified with a maximum of 200 m (660 feet), depending on the diameter of the sewer section to be rehabilitated and the existing damages. Under favorable conditions, even longer sections can be rehabilitated in one process step. The sewer to be rehabilitated should have no bends and angular deflections [DWA-M 143-9:2019-11]. By the use of special plastics profiles that have a so-called
expansion joint |
|
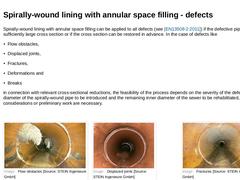
Spirally-wound lining with annular space filling can be applied to all defects (see [EN13508-2:2011]) if the defective pipeline has a sufficiently large cross section or if the cross section can be restored in advance. In the case of defects like -
Flow obstacles,
-
Displaced joints,
-
Fractures,
-
Deformations and
-
Breaks
in connection with relevant cross-sectional reductions, the feasibility of the process depends on the severity of the defects, the … |
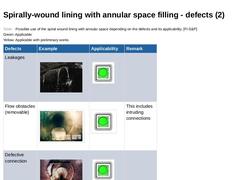
|
(Table: Possible use of the spiral wound lining with annular space depending on the damages) |

|
Spiral wound lining without annular space filling can only be applied to defects in which the original cross-section is given or can be restored in advance (see EN 13508-2) . Such defects are leakages, mechanical abrasion, corrosion and cracks; exception of these are smaller socket misalignments. In the case of defects in connection with cross-sectional reductions, such as socket (joint) misalignments, appropriate preparatory works … |

|
The following 3 illustrations are defect examples which would need to be corrected prior to the spiral wound lining. (Image: Displaced joint (positional deviation)) (Image: Pipe break – Pieces of pipe lie on the invert) Flow obstacles (must be removed) Displaced joints (horizontally) (leads to a cross-section reduction) Pipe breaks (presupposes the stability of the cleared section during rehabilitation / after removal of the fragments, … |

|
(Image: Function of manholes - Accessibility - Access for persons) Another requirement for the application of spiral wound lining in non-man-accessible drains and sewers is the accessibility of the starting and target manhole; with man-accessible drains and sewers the accessibility of the starting manhole is sufficient. In both cases the existing manholes are used [DWA-M 143-9:2019-11]. |

|
|

|
For the planning of the works a careful recording of the actual state of the existing sewer is to be carried out in order to determine whether spiral wound lining may be used to renovate the sewer, taking into account the technical feasibility. All planning documents are to be made available to the executing company by the client or network operator. |

|
(Image: Picto Liste) An accurate and complete pipeline condition assessment (PCA) must be determined by the planner. The PCA should provide the following information on the existing pipelines: -
Pipe material and wall thicknesses,
-
Differences in internal diameter,
-
Changes of direction and connections,
-
Soil conditions (e.g. soil type, cover, max/min groundwater level, modulus of deformation),
-
Damages, particularly, -
Positional deviations,
-
Root ingress,
|

|
The following information about the old sewer should be available: For masonry sewers additional information is required: wall thickness (possibly variable over the circumference), mortar and brick strength (also distributed over the wall thickness), design of the invert (… |

|
|
|
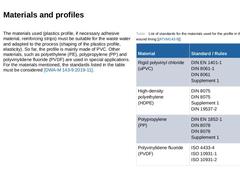
The materials used (plastics profile, if necessary adhesive material, reinforcing strips) must be suitable for the wastewater and adapted to the process (shaping of the plastics profile, elasticity). So far, the profile is mainly made of uPVC (polyvinyl chloride). The "u stands for "unplasticised". Other materials, such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP) and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are used in special applications. (Image: Extruded profile … |
|
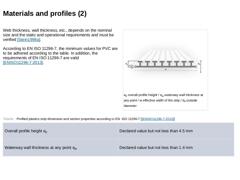
Web thickness, wall thickness, etc., depends on the nominal size and the static and operational requirements and must be verified [Stein1998a]. According to EN ISO 11296-7, the minimum values for PVC are to be adhered according to the table. In addition, the requirements of EN ISO 11296-7 are valid [ENISO11296-7:2013]. (Image: Example of a profiled plastics strip without seam) (Table: Profiled plastics strip dimension and section properties according … |

|
|

|
The general working sequence of spiral wound lining includes the processes (Image: Working sequence for the renovation of drains and sewers with site manufactured pipes - spiral wound lining) |

|
(Table: Preliminary works for the spirally-wound pipe process) Before the rehabilitations work begins, the sewer to be rehabilitated must be cleaned and optically inspected. In addition, the diameter of the sewer section at the end and starting point and the length of the sewer section are to be measured. (Image: High-pressure cleaning of the sewer section) (Image: Inspection of the sewer section) (Image: Sketch of principle of a TV inspection of the … |

|
(Table: Preliminary works for the spirally-wound pipe process (2)) -
The existing lateral drains and sewers are to be measured according to their position and diameter (image left). Intruding obstacles have to be removed (images in the middle).
-
The determine the maximum possible diameter for the spirally-wound pipe, a calibration of the sewer section to be rehabilitated should be carried out (image right).
(Image: Inspection of the lateral drain) (… |

|
(Table: Preliminary works for the spirally-wound pipe process (3)) -
When the cement-based grout in the annular space between the spiral wound pipe and the host sewer assumes a static function, the concerned sewer section has to be sealed against water infiltration in advance to prevent uncontrolled mixing of the grout with groundwater.
-
When the cement-based grout in the annular space between the spiral wound pipe and the host sewer only takes over …
|

|
(Table: Preliminary works for the spirally-wound pipe process (4)) (Image: Preparation of the manhole for the rehabilitation) (Image: Lowering the single components of the winding machine into the starting manhole) |

|
No securing of the drainage capability required! When using the spiral wound lining, the drainage capability can generally be maintained in the sewer to be rehabilitated. When required, the existing invert might need to be modified so that the winding machine can be placed to accommodate the necessary manhole connections and be aligned accurately for the liner installation. In order to guarantee a successful spiral wound lining process, … |

|
However, it must be ensured that the joining at which the lock profiles are connected to each other is always above the water level. If this is no longer guaranteed or if the water level exceeds a height of approx. 40% of the clearance height of the sewer cross section, the works has to be interrupted. Before restarting the winding process, the winding machine must be cleaned carefully. The plastics profile, which has remained in the sewer during … |

|
If, in the case of an increase of the water level above the previously mentioned level the works continues, at least for the drainage quantity exceeding the limit value, a securing of drainage capability must be set up for the duration of the winding process [DWA-M 143-9:2019-11]. If provisional closing elements (e.g. sealing packers and discs) are installed as part of the securing the drainage capability, they must always be supported in the manhole … |