
|

| (Image: Lining with cured-in-place pipes)
|
|

|

|

|

| (Image: Attention!)
The application of the cured-in-place lining process requires a thorough determination of the actual state of the old-pipe-soil-system. The rehabilitation object still has to be stable and has to allow the insertion of the soaked hose. The hydraulic efficiency has to be analyzed since the cross section of the drain is reduced by using the cured-in-place lining process. |
|
|

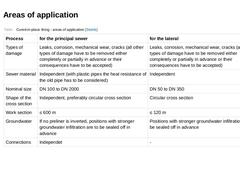
(Table: Cured-in-place lining - areas of application [Steinb]) |
|

|

Applicable |
(Image: Corrosion of the whole inner surface of a concrete sewer - Camera picture [FI-IfK])
|
(Image: Root ingress)
|
(Image: Picture of a damage 'collapse' of a section of a vitrified clay stormwater sewer DN/ID 300 – Argus4-picture taken at 28.4 m)
|
The cured-in-place lining process can be applied in gravity- and pressure pipelines for damage types like leaks, corrosion, root ingress and cracks. | Conditionally applicable |
|

|

|
|

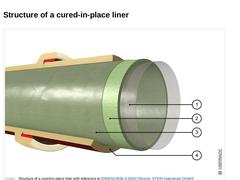
| (Image: Structure of a cured-in-place liner with reference to [DINEN13566-4a] [Image: S&P GmbH])
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
Old sewer - Putting out of operation (securing of drainage capability)
- Cleaning
- Optical inspection
- Removal of roots, deposits and other drainage obstacles
- Probable sealing of groundwater infiltrations
- Measurement and calibration of the section that is to be rehabilitated
- Probable creation of an excavation for installation (dependent on nominal size)
| |
(Image: Cleaning)
|
|
(Image: Inspection)
|
|
(Image: Damages)
|
|
|

|

|

|

|
Before inserting the liner, a thin PE foil hose, also called Preliner hose or Preliner is installed in most European countries as a basic measure . |
(Image: Installation of the Preliner)
|
|
(Video: Insituform process: Inversion of the preliner [FI-Insit])
|
The object of this is to prevent, among others the - Ingress of un-hardened resins in soil and groundwater;
- Uncontrolled ingress of so-called "excess" resin into connection regions where it could lead …
|
|

|

| Eversion (Inversion) (Image: Insertion of the liner hose by means as an example with the Insituform process)
Everted-in-place insertion:
Method whereby the impregnated liner is introduced by eversion to achieve simultaneous insertion and inflation [DINEN13566-4:2003]. | | Pulling-in process (Image: KM-Inliner process with reference to [FI-KMG] - Sketch of principle of pulling-in the liner [Image: S&P GmbH])
Winched-in-place insertion:
Method whereby the … |
|

|

| EN 13566-1 / DWA-M 143-3 Curing:
Process of resin polymerisation, which may be initiated or accelerated by the use of heat or exposure to light [DINEN13566-4:2003]. | | | (Image: Controlling and documenting the supply and return temperatures)
| (Image: Light source)
|
Polymerization: Mounting of molecules by chemical bonds into a new substance. |
|

|

|
The hardening of the soaked hose can be carried out depending on the cured-in-place liner system: - in environmental temperature (cold hardening),
- by adding heat (thermal hardening) or
- by UV-light (light hardening).
|
(Image: KM-Inliner process with reference to [FI-KMG] - Thermical hardening)
|
(Image: Inpipe process with reference to [FI-Teerb] - Light hardening with UV heating lamps [Image: S&P GmbH])
|
|
|
|

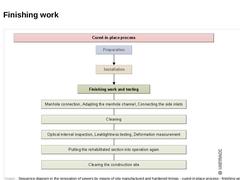
| (Image: Sequence diagram in the renovation of sewers by means of site manufactured and hardened linings - cured-in-place process - finishing work)
|
|

|

|
(Image: Connecting the liner into the entry manhole with reference to [FI-Insit] - View of the manhole connection [Image: S&P GmbH])
|
|
(Image: Lateral connection by means of a top hat sleeve)
|
- Manhole connections
- Fitting of the cured-in-place liner to the manhole channel
- Reconstruction of the inclusion of the laterals
|
|

|

|
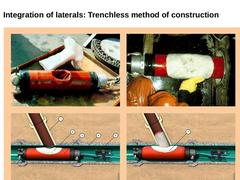
Open cut method: The integration of laterals to the cured-in-place lined sewer is carried out via small excavations. For that purpose the integration points in the sewer have to be measured accurately in advance. (Image: Sewer opening by means of core drilling in the open cut method)
| |
Trenchless method The connection region is relatively easy to recognise from inside. In this region the liner bulges outwards somewhat so that boring, cutting and milling … |
|
|

| |
(Image: Recreation of the branch connection [FI-Insit] - Packer and top hat sleeve)
|
(Image: Recreation of the branch connection [FI-Insit] - Packer with inverted top hat sleeve before installation)
|
|
(Image: Recreation of the branch connection - Description of the process with reference to [FI-Insit] [Image: S&P GmbH])
|
(Image: Recreation of the branch connection - Description of the process with reference to [FI-Insit] [Image: S&P GmbH])
|
|
|

|

- Check and documentation of the cleaning, inspection, measurement and calibration of the sewer section that is to be rehabilitated.
- Reception control of the hose.
- Protocol of the transportation- and storage temperature (dependent on procedure).
- Recording of the tensile force during the pulling-in of the preliner- and liner hose.
- The hardening procedure is to be observed from a metrological point of view and is to be documented in a protocol.
- Taking …
|
|

|

- Construction site personnel 3-5 people
- Cooling box or light-proof box or soaking facility depending on the type of liner
- Heating aggregate, steam generator or light source
- Pulling-in- or eversion system (frame or drum)
- possibly lifting device
(Image: Equipment for lining with cured-in-place pipes) |
|

|

|

|

| (Image: Pros and cons) | - Short period of construction
- Installation above the manhole construction
- Independency from material and shape of the cross section
- Applicable in non-accessible and accessible area
- Adjustable to different chemical demands
- Bends and angular deflections can be rehabilitated
- Inclusion of side inlets possible in the trenchless method of construction
- Small reduction of the cross section
- No pipe joints
- Improvement of the structural …
|
|

|

| (Image: Pros and cons) | - It is necessary to take the sewer out of operation
- Development of folds in the case of severe alterations of dimension and angular deflections
- Inner outline of the cured-in-place liner is determined by the surface structure of the old pipe
- Ovalties of the old pipe reduce the structural load bearing capacity
- Unprofessional soaking can lead to leaks
- Handling of liquid resin on the construction site
|
|